4.6.4. Depth of investigation (DOI) calculation
With the DOI Workflow, the user can compare two models in order to
estimate the robustness of geophysical anomalies. The resulting DOI index can be
visualized and used as weights in subsequent inversions.
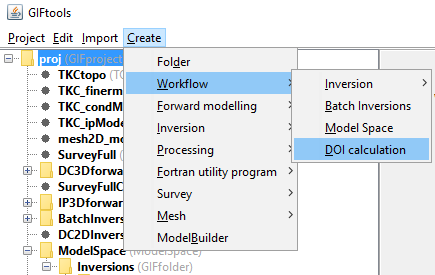
Create → Workflow → DOI calculation
4.6.4.1. Edit Options
DOI calculations follow the work presented in Li & Oldenburg 1999. The calculation requires two models and their respective reference values.
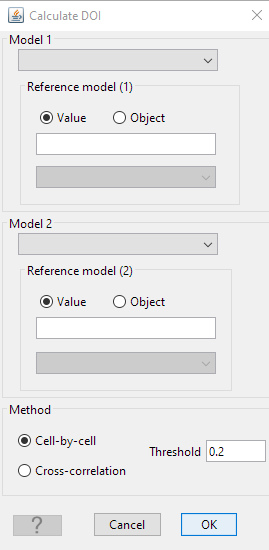
- model 1 (& 2)
inverted models with two different reference models
- reference 1 (& 2)
reference models used in the inversion
- method
option 1: Cell-by-cell. The first method looks at the deviation of models normalized by the difference in reference value on a cell-by-cell basis:
\[R(x,y) = \frac{m_1(x,z) - m_2(x,z)}{m_1^{ref}-m_2^{ref}}\]where \(m_1\) and \(m_2\) are the two chosen models and \(m^{ref}_1\) and \(m^{ref}_2\) their respective background referencemodels. Model parameters with large R values are assign high credibility.
option 2: Cross-correlation: The second strategy measures the difference between two images over n cells in a rectangular window. The cross-correlation between the two models are calculated as
\[C = \frac{ \sum_i^N (m_{1_i}-\bar m_{1}) (m_{2_i}-\bar m_{2})}{\bigg( \sum_i^N (m_{1_i}-\bar m_{1})^2 \sum_i^N (m_{2_i}-\bar m_{2})^2\bigg)^{(1/2)}}\]where \(\bar m\) is the average of the model over the window. The DOI index is calculated by
\[R = \frac{C-1}{2}\]
- threshold
Threshold used on the DOI to cut the models.
4.6.4.2. Output
- reference model 1 (& 2)
reference models used for the computation
- DOI:
Computed DOI
- DOI_Thresholded
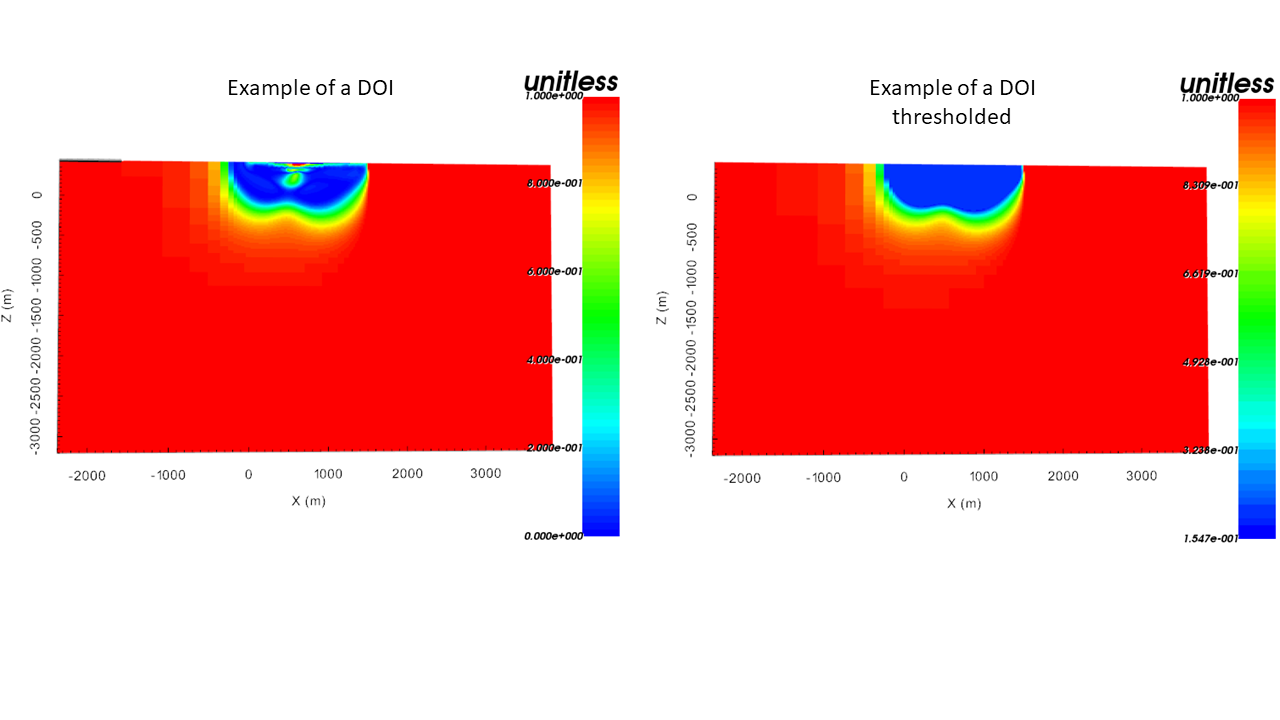
DOI model which has been thresholded (with the input thresold) at the surface to highlight the area of interest (see figure below for an example).
- DOI_Masked_model1 (&2)
Model masked based on the thresholded DOI.