5.1.19. MT / ZTEM data: MTZ3D GIF file
This file is the structure for MT and/or ZTEM data associated with the inversion program MTZ3D. The type of data is set by a data flag. Data that should be ignored are denoted by an i. The general format is:

Parameter definitions:
DT: The data type flag. The flagDATATYPEpreceeds this input. The options for the data flag are:MTZ: MT data; impedance data with both imaginary and real parts.MTR: MT data; apparent resitivities and phasesMTT: ZTEM data; real and imaginary tipper functions is absolute ratio. Hx and Hy are constant at the reference (base) station location. This is the most typical flag for ZTEM data.MTB: Both MT and ZTEM data; ZTEM data is denoted by providing a reference (base) station after the frequency declaration.
flg: Any value that does not contain actual data. By default, GIFtools will exportNaNas the ignore value. The flagIGNOREpreceeds this input.FREQ: The frequency for the data type.nRec: Number of receivers associated with the given frequency.[\(BaseX_{[j,k]} ...\)]: This line is only present for ZTEM data. The line consists of the (X,Y,Z) for the base station followed by “i” (usually 8 columns) for the number of data columns given on the next line.
[\(X_{[j,k]} ...\)]: Easting (m) of the \(k^{th}\) receiver for the \(j^{th}\) data type.
[\(Y_{[j,k]} ...\)]: Northing (m) of the \(k^{th}\) receiver for the \(j^{th}\) data type.
[\(Z_{[j,k]} ...\)]: Elevation (m) of the \(k^{th}\) receiver for the \(j^{th}\) data type.
data: Columns of data / uncertainty pairs depending upon the data type:Impedence MT data: The 16 data columns are in MT coordinates (X+ north, Y+ East, Z+ down) and consist of the following in order:
\(ZXX^r\): Real part of the ZXX component
\(ZXX^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the real part of the ZXX component
\(ZXX^i\): Imaginary part of the ZXX component
\(ZXX^i_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the imaginary part of the ZXX component
\(ZXY^r\): Real part of the ZXY component
\(ZXY^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the real part of the ZXY component
\(ZXY^i\): Imaginary part of the ZXY component
\(ZXY^i_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the imaginary part of the ZXY component
\(ZYX^r\): Real part of the ZYX component
\(ZYX^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the real part of the ZYX component
\(ZYX^i\): Imaginary part of the ZYX component
\(ZYX^i_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the imaginary part of the ZYX component
\(ZYY^r\): Real part of the ZYY component
\(ZYY^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the real part of the ZYY component
\(ZYY^i\): Imaginary part of the ZYY component
\(ZYY^i_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the imaginary part of the ZYY component
Apparent resistivity / phase MT data: The 16 data columns consist of the following in order (phase in degrees and apparent resistivity in Ohm-m):
\(ZXX^r\): ZXX component of apparent resistivity
\(ZXX^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the ZXX component of apparent resistivity
\(ZXX^p\): ZXX component of phase
\(ZXX^p_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the ZXX component of phase
\(ZXY^r\): ZXY component of apparent resistivity
\(ZXY^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the ZXY component of apparent resistivity
\(ZXY^p\): ZXY component of phase
\(ZXY^p_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the ZXY component of phase
\(ZYX^r\): ZYX component of apparent resistivity
\(ZYX^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the ZYX component of apparent resistivity
\(ZYX^p\): ZYX component of phase
\(ZYX^p_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the ZYX component of phase
\(ZYY^r\): ZYY component of apparent resistivity
\(ZYY^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the ZYY component of apparent resistivity
\(ZYY^p\): ZYY component of phase
\(ZYY^p_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the ZYY component of phase
ZTEM data: The 8 data columns are in MT coordinates (X+ north, Y+ East, Z+ down) and consist of the following in order:
\(ZXY^r\): Real part of the ZXY component
\(ZXY^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the real part of the ZXY component
\(ZXY^i\): Imaginary part of the ZXY component
\(ZXY^i_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the imaginary part of the ZXY component
\(ZYX^r\): Real part of the ZYX component
\(ZYX^r_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the real part of the ZYX component
\(ZYX^i\): Imaginary part of the ZYX component
\(ZYX^i_{stn}\): Standard deviation of the imaginary part of the ZYX component
NOTE: When using the MTB flag for both data, the locations will include both MT and then ZTEM data and must be in impedances. Therefore, MT data would follow with 8 columns of the ignore flag and ZTEM data would have 16 columns of ignore flag prior to data (see example 3 below).
5.1.19.1. Examples
The following are two examples of data files.
Example 1: Off-diagonal (ZXY and ZYX) impedance MT data at 3 frequencies (100, 10, and 1 Hz) with 2 observations each for brevity:

Example 2: ZTEM data at 2 frequencies (30 and 45 Hz) with 3 observations each with a single base station:
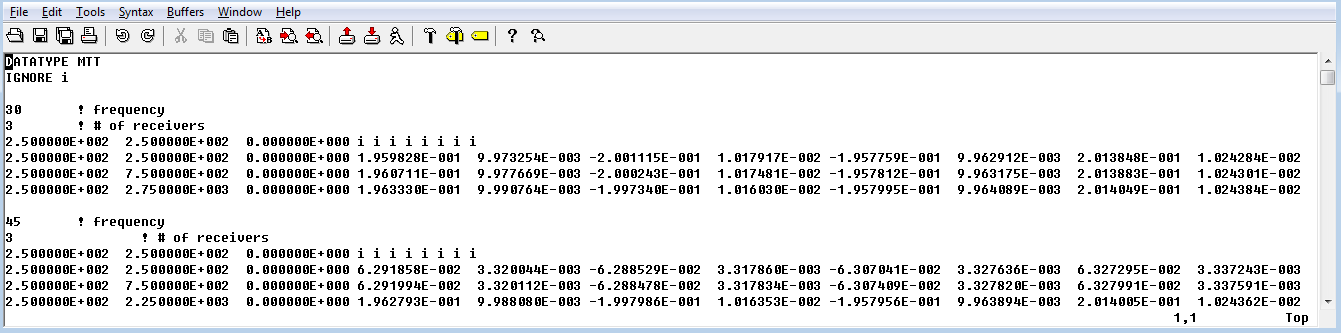
Example 3: MT and ZTEM data (combining example 1 and example 2). Note that the MT data comes first and then the ZTEM data:
